LIVER
In Vitro toxicity assay in cell lines
Drug screening is a long and costly process. It is big challenge in using animals as model to confirm with low productivity. It limits the discovery of new drugs. To reduce the number of animals in tests and to accelerate drug discovery process, recent efforts have been dedicated to developing cell-based high throughput screening. It helps to improve and fasten the drug screening process. It provides more relevant to in vivo biological information. The data obtained from tissue culture help pharma industry to determine potential efficacy and safety (e.g., predictive toxicity) of drug candidates. In vitro cell culture also provides information about morphology and cellular functions such as cell-cycle status, health and viability, and cell signaling pathways in drug discovery. We provide these services as per the industry requirement.
Most common service we provide in the cell lines are
- Cell viability
- Cell cytotoxicity
- Apotosis assay (Caspase 2,3,6,7,8 and 9 assay)
- Cancer research
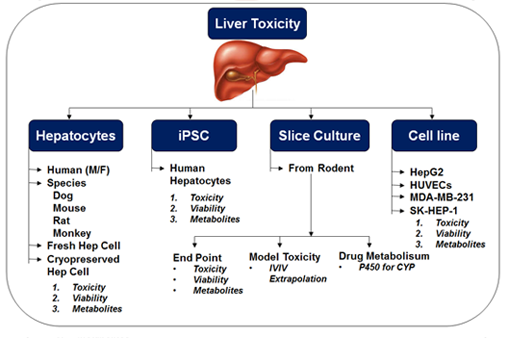
Toxicity study with primary culture of human and animal hepatocytes and also in induced pluripotent stem cells (IPSC)
Stem cells are distinct self-replenishing cell population whose primary function is to generate progeny that develop into terminally differentiated cell types, such as a cardiomyocytes, neurons or receptors. This ability of cells known as “pluripotency” is a hallmark of embryonic stem cells (ESCs). Stem cells belong to one of two major categories according to their potency of differentiation: organ-specific stem cells and pluripotent stem cells. Organ-specific stem cells generally have limited potential for growth and differentiation. In contrast, pluripotent stem cells, such as ESCs and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) replicate in culture dishes and are theoretically capable of giving rise to any of the cell types found in the body.
Most of the drug fails at preclinical stage because of liver toxicity and alterations of hepatic physiology. In addition, drug-induced liver injury is the most common reason for market withdrawal of approved drugs due to safety concerns. It is really difficult to predict liver toxicity because lack of biologically relevant and predictive model systems. Stem cells of hepatocytes will overcome these limitations and provide well-characterized, highly reproducible, and readily available human hepatocytes for preclinical drug development and safety testing.
Drik provide services for human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes and hepatocytes. These human cardiac and hepatocytes cells are specifically designed to aid drug discovery and improve the predictability against structurally diverse drugs. They help researchers to better understand and optimize the predictive algorithm for applications in discovery toxicology, cardiac and liver safety screening. We obtained these iPSC from reliable source of well-characterized, highly reproducible, and readily available for preclinical drug development and safety testing.
Mechanistic toxicology
To understand mechanism of action, the following assay end points are offered by Drik:
Cell viability
- MTT
- Neutral red
- LDH
Cell death
- Propidium iodide
- Fluorojade B
CYP inhibition CYP induction; DDI
Mitochondrail toxicity
Phospholipidosis; Steatosis
Apoptosis (Casp3/7/8/9), BrDU
Autophagy
Necrosis
GSH; Oxygen radical absorbance
Screening panel

Privacy & Policy/ Terms & Condition